Davisson-Germer Experiment
Davisson-Germer Experiment: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Davisson-Germer Experiment, Experimental Verification of Wave Nature of Matter, Wave Nature of Electrons and Diffraction of Electron.
Important Questions on Davisson-Germer Experiment
What is the significance of Davisson- Germer experiment?
The wave nature of electrons was verified by
What was the purpose of Davisson-Germer experiment?
What do you understand by diffraction of electron?
Briefly explain the working of Davisson and Germer experiment.
What do you mean by diffraction of electron?
What was the purpose of Davisson-Germer experiment?
What do you mean by diffraction of electron?
In the Davission and Germer experiment, what is the phenomenon of the electrons that is observed?
Match list-I (Fundamental Experiment) with List-II (its conclusion) and select the correct option from the choices given below the list:
| List-I | List-II | ||
| A | Franck-Hertz Experiment | (i) | Particle nature of light |
| B | Photo-electric experiment | (ii) | Discrete energy levels of atom |
| C | Davison-Germer Experiment | (iii) | Wave nature of electron |
| D | (iv) | Structure of atom |
In Davisson - Germer experiment maximum intensity is observed at
Davisson and Germer experiment proved
The correct relation between the angle of diffraction and the glancing angle in Davidson – Germer experiment will be
Wave property of electrons implies that they will show diffraction effects. Davisson and Germer demonstrated this by diffracting electrons from crystals. The law governing the diffraction from a crystal is obtained by requiring that electron waves reflected from the planes of atoms in a crystal interfere constructively (see figure).
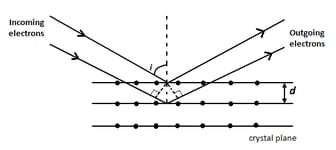
If a strong diffraction peak is observed when electrons are incident at an angle from the normal to the crystal planes with distance between them (see figure), de Broglie wavelength of electrons can be calculated by the relationship ( is integer)
